OPGW (Optical Ground Wire)

OPGW (Optical Ground Wire): The Backbone of Modern Power & Communication Networks
In today’s interconnected world, power transmission systems are no longer just about electricity—they are also vital communication highways. OPGW (Optical Ground Wire) has emerged as a revolutionary solution that combines electrical grounding with high-speed fiber optic communication. Widely used in overhead transmission lines, OPGW plays a crucial role in modern smart grids, telecom integration, and utility infrastructure.
This blog explores what OPGW is, how it works, its structure, applications, benefits, and why it is essential for future-ready power networks.
What is OPGW (Optical Ground Wire)?
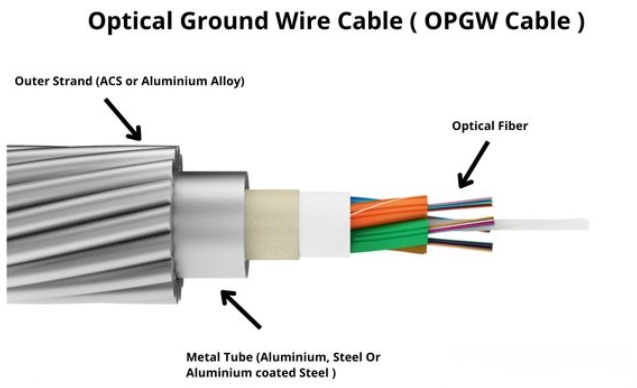
OPGW (Optical Ground Wire) is a specialised cable installed at the top of high-voltage overhead transmission lines. It serves two primary functions:
- Grounding and lightning protection for power lines
- High-speed fiber optic communication for data transmission
Unlike traditional ground wires, OPGW contains optical fibers embedded within its metallic structure, allowing power utilities to transmit voice, data, SCADA signals, and protection relays without installing separate communication cables.
Structure and Construction of OPGW Cable
The unique design of OPGW enables it to withstand harsh environmental and electrical conditions while protecting delicate optical fibers.
Key Components of OPGW
- Optical Fibers
Single-mode fibers (commonly ITU-T G.652 or G.655) placed in stainless steel or aluminum tubes - Central or Layered Design
Fibers may be placed in the core or distributed in layers - Aluminum Alloy / Aluminum-Clad Steel Wires
Provide mechanical strength and conductivity - Stainless Steel Tube (SST)
Protects fibers from moisture, pressure, and temperature variations
This robust construction ensures high tensile strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and long service life.
How Does OPGW Work?
OPGW is installed at the top of transmission towers, replacing conventional earth wires. Its metallic outer layers conduct lightning strikes safely to the ground, protecting the phase conductors below.
At the same time, the optical fibers inside the cable transmit data signals, enabling:
- Real-time grid monitoring
- Power system protection
- Telecommunication services
- Substation automation
This dual-function design makes OPGW highly efficient and cost-effective.
Applications of OPGW Cable
OPGW is widely used across power and communication sectors.
1. Power Transmission Lines
OPGW is standard in high-voltage (HV), extra-high voltage (EHV), and ultra-high voltage (UHV) transmission lines.
2. Smart Grid Communication
Supports SCADA, EMS, and real-time fault detection systems.
3. Telecommunication Networks
Utilities lease excess fiber capacity to telecom operators for broadband and data services.
4. Substation Automation
Ensures reliable and fast data exchange between substations.
5. Renewable Energy Integration
Used in wind farms, solar plants, and long-distance power evacuation projects.
Advantages of OPGW (Optical Ground Wire)
1. Dual Functionality
Combines grounding and communication in a single cable, eliminating the need for separate infrastructure.
2. High Reliability
Protected fibers ensure minimal signal loss and long-term performance.
3. Cost Efficiency
Reduces installation, maintenance, and right-of-way costs.
4. Enhanced Grid Security
Provides fast fault detection and system protection.
5. Environmental Resistance
Designed to withstand wind, ice loads, lightning, and extreme temperatures.
6. Long Service Life
Typically lasts 30–40 years with minimal maintenance.
OPGW vs ADSS: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | OPGW | ADSS |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Location | Top of tower | On side of tower |
| Electrical Grounding | Yes | No |
| Lightning Protection | Excellent | Limited |
| Mechanical Strength | Very High | Moderate |
| Best Use Case | Transmission lines | Distribution lines |
OPGW is preferred for high-voltage transmission, while ADSS is suitable for lower-voltage or telecom-only applications.
Installation and Maintenance of OPGW
Installation
OPGW is installed using tension stringing methods, often while replacing existing ground wires. Installation requires careful planning to avoid fiber damage.
Maintenance
- Periodic visual inspection
- Optical attenuation testing
- Hardware and joint box checks
Thanks to its durable design, OPGW requires minimal maintenance over its lifetime.
Standards and Specifications
OPGW cables are manufactured according to international standards such as:
- IEC 60794
- IEEE 1138
- ITU-T Fiber Standards (G.652, G.655)
- ASTM and EN standards for mechanical and electrical properties
Compliance ensures safety, reliability, and global compatibility.
Why OPGW is Essential for Future Power Networks
With the rise of smart grids, IoT-based monitoring, and renewable energy, power networks require fast, secure, and reliable communication. OPGW enables utilities to:
- Monitor grid health in real time
- Improve fault response time
- Enhance power quality
- Support digital transformation
As energy systems become more complex, OPGW stands as a critical infrastructure component bridging power and data.
Choosing the Right OPGW Cable
When selecting OPGW, consider:
- Number of optical fibers
- Tensile strength requirements
- Short-circuit current capacity
- Environmental conditions
- Compliance with relevant standards
Partnering with a reliable OPGW manufacturer ensures optimal performance and long-term reliability.
Conclusion
OPGW (Optical Ground Wire) is more than just a grounding conductor—it is the backbone of modern power and communication networks. By integrating lightning protection with high-speed fiber optics, OPGW enables utilities to build smarter, safer, and more efficient transmission systems.
As global demand for reliable electricity and data connectivity continues to grow, OPGW will remain a cornerstone of future-ready power infrastructure.
For such comprehensive blogs, click here Life Cables Blogs.