Categories of Electric Cables (by Voltages):

Voltage Categories
- Low Voltage (up to 750 V): Versatile cables with thermoplastic or thermoset coatings, built to harmonized standards.
- Low Voltage (up to 1,000 V or 0.6/1 kV): Used for industrial power in various sectors, adhering to international standards (UNE, IEC, BS, UL).
- Medium Voltage (1 kV to 36 kV): Distributes electricity from substations to transformer stations.
- High Voltage (from 36 kV): Transports electricity from generating plants to substations.
Types of Electrical Cables by Use
- Low Voltage Cables:
- Cables for electric panels: Flexible, ideal for domestic use, public places, and internal wiring of electrical cabinets and small appliances.
- Power cables: For industrial and public facility power transmission in low voltage connections and variable frequency drives (VFDs).
- Armoured cables: Have aluminum or steel reinforcement for protection against mechanical damage, rodents, and in fire/explosion risk (ATEX) environments.
- Rubber cables: Extra flexible, used in fixed industrial installations and mobile services. Welding cables typically have rubber sheaths for high current transmission.
- Halogen-free cables (LSZH): Low smoke and corrosive gas emission in fire, suitable for electrical panels, public places, emergency circuits, and mobile service.
- Fire resistant cables: Designed to transmit power during prolonged fires, ensuring supply to emergency equipment like alarms, smoke extractors, and pumps.
- Control cables: Extremely flexible, for small household appliances, machine interconnection, signaling, motor connections, and avoiding electromagnetic interference.
- Instrumentation cables: Flexible, shielded, for signal transmission in high electromagnetic interference industrial settings.
- Solar cables: Connect photovoltaic panels to inverters, resistant to solar radiation and extreme temperatures for outdoor installation.
- Special cables: For specific uses like temporary lighting, cranes, hoists, lifts, submerged pumps, and aquatic systems.
- Aluminum cables: For fixed power transmission indoors, outdoors, or underground.
- Medium Voltage Cables:
- RHZ1 cables: XLPE insulated, halogen-free, non-flame propagating for energy distribution.
- HEPRZ1 cables: HEPR insulated, halogen-free, non-flame propagating for energy distribution.
- MV-90: XLPE insulated, American standard compliant for energy distribution.
- RHVhMVh cables: Copper and aluminum, for applications with oil and chemical agent risks.
Components of an Electrical Cable
- Electric conductor: Channels electricity (bare wire, aluminum, copper, flexible copper wire). Can be single-core or multi-core.
- Insulation: Covers the conductor to prevent current leakage (thermoplastic like PVC, Z1, PE, PU; or thermosetting like EPR, XLPE, EVA, SI, PCP, SBR).
- Auxiliary elements: Protect the cable and ensure longevity.
- Outer sheath: External layer protecting all components.
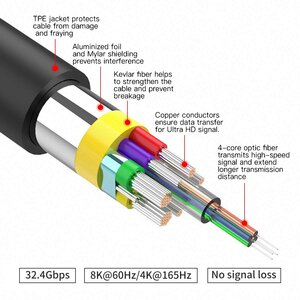
Metal Protections for Electrical Cables
- Screens: Electrical metal protections to isolate internal signals from external interference.
- Armours: Mechanical protections against external aggressions (animals, impacts).
Electrical Cable Nomenclature
Cables have a standard designation (letters and numbers) indicating characteristics like materials and nominal tensions. This helps in selecting the correct cable.
- Insulation: R (XLPE), X (XLPE), Z1 (Halogen-free thermoplastic polyolefin), Z (Halogen-free thermosetting elastomer), V (PVC), S (Halogen-free thermosetting silicone), D (EPR).
- Screen/Lining/Armature Seat: C3 (Copper wire screen, helical), C4 (Copper braid screen), V (PVC), Z1 (Halogen-free thermoplastic polyolefin). (No letter if absent).
- Armour: F (Steel strapping, helical), FA (Aluminum strapping, helical), FA3 (Corrugated aluminum strip), M (Steel wire crown), MA (Aluminum wire crown).
- Outer Sheath: V (PVC), Z1 (Halogen-free thermoplastic polyolefin), Z (Halogen-free thermosetting elastomer), N (Vulcanized chlorinated polymer).
- Conductor: K (Flexible copper class 5, fixed), F (Flexible copper class 5, mobile), D (Flexible for welding). (No letter for solid copper class 1 or 2). (AL) for aluminum.
- Rated Voltage: 0.6/1 kV (1,000V).
- Conductor Count: nG (number and cross-section with Yellow/Green conductor), n (number and cross-section without Yellow/Green conductor).
- Design Rules: UNE 21123, IEC 60502, UNE 21150.
- Additional Data: CE (CE marking), Date of Manufacture (YYMMDD).
Dimensioning Criteria of Electrical Conductors
- AWG (American Wire Gauge): Conductors defined by number and diameter of wires.
- European Sizing (mm²): Conductors defined by maximum resistance (Ω/km). Solid or flexible conductors are defined by minimum wire count or maximum wire diameter.
Electrical Cable Measurements
| Cross-Section (mm²) | AWG | Current Consumption | Used For | | :—————— | :– | :—————— | :——- | | 25 | 4 | Very high | Central air conditioning and industrial equipment. | | 16 | 6 | High | Air conditioners, electric stoves, and electric power connections. | | 10 | 8 | Medium high | Refrigerators and dryers. | | 6 | 10 | Medium | Microwave and blenders. | | 4 | 12 | Medium | Lighting. | | 2.5 | 14 | Low | Lamps. | | 1.5 | 16 | Very low | Thermostats, bells, or security systems. |
Types of Colours in Electrical Cables and Their Meaning
Colors follow IEC 60446: black, brown, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, gray, white, pink, and turquoise.
Protective or earthing conductor: Yellow and green (yellow or green single-colored cables are only permitted if no confusion with earthing).
Neutral conductor: Blue (avoid other blue conductors).
Phase conductor: Black, grey, or brown.